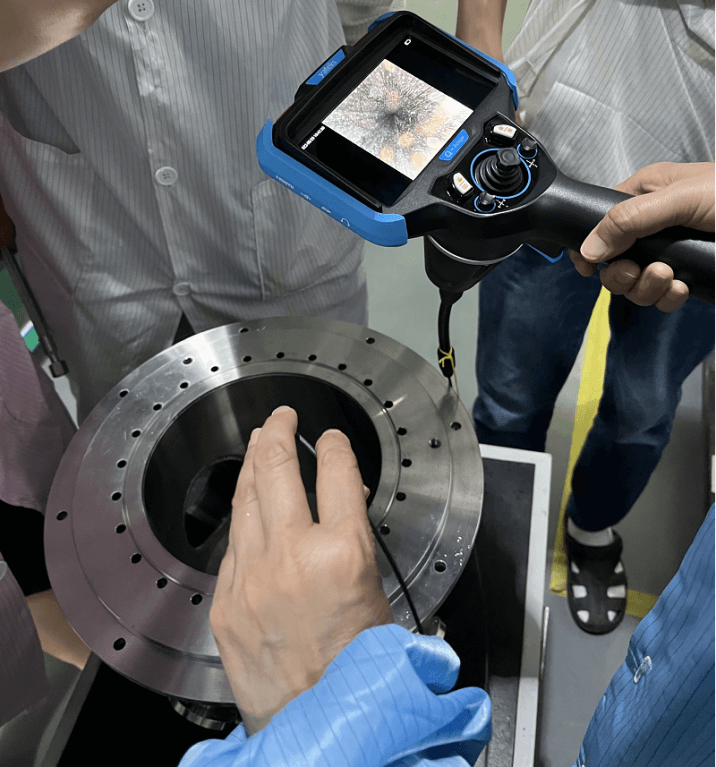
What is a borescope?
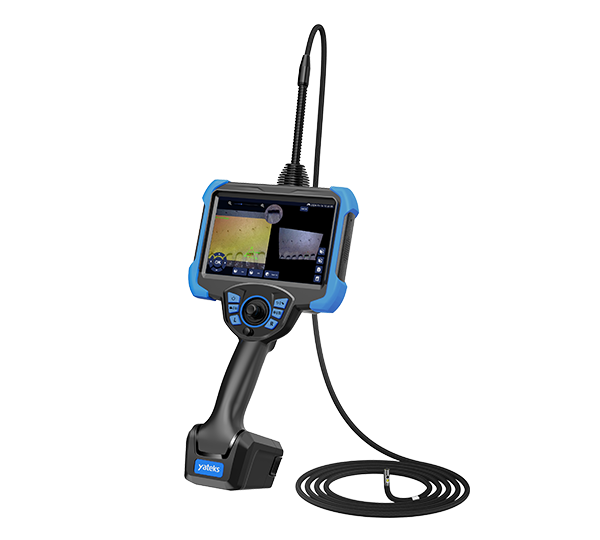
A borescope is a type of remote visual inspection device that consists of a rigid or flexible tube that transmits images back to an ocular or screen. Inspectors use these devices to look inside difficult-to-access areas.
What is the difference between a videoscope and a borescope?
Videoscope are a type of borescope. Borescopes are simpler instruments with fewer features. Videoscopes are versatile, durable visual inspection tools. it offer many leading-edge features, including video/still image recording.
How do videoscopes and borescopes work?
Videoscopes have a small sensor chip in the tip of their insertion tubes. it enables them to capture video and still images. The sensor sends these images to an LCD screen where they are viewed by the inspector. Many modern videoscopes also have an LED or laser diode light source. It located in the tip of the insertion tube. Borescopes are simpler instruments that transmit images through a flexible or rigid insertion tube back to an ocular or screen.
What is the difference between a borescope and an endoscope?
Industrial endoscopes and videoscopes are interchangeable terms. and both refer to the same type of instrument. Endoscopes/videoscopes are a more advanced type of borescope. They has video and still image recording capabilities.
What are the application areas of industrial endoscopes?
In general, industrial endoscopy is widely used in various industries. involving the development and manufacture of machinery. and chemical industry, automobile manufacturing, aerospace, railway engineering vehicles, and transportation vehicles, maintenance and repair and other fields. Industrial endoscopes can also find applications in the infrastructure process of projects. such as the construction of bridges and tunnels, and in maintenance.
How to use the 2D measurement function of the Q series industrial endoscope?
First of all, the meaning of 2D comparison measurement . in the same plane, through a known value, we can compare and measure another unknown value in the plane.
Therefore, there are 3 prerequisites for using this function, 1. There must be a reference object and measured object 2. The actual value of the reference object must be known, 3. The reference object and measured object must be in the same plane.
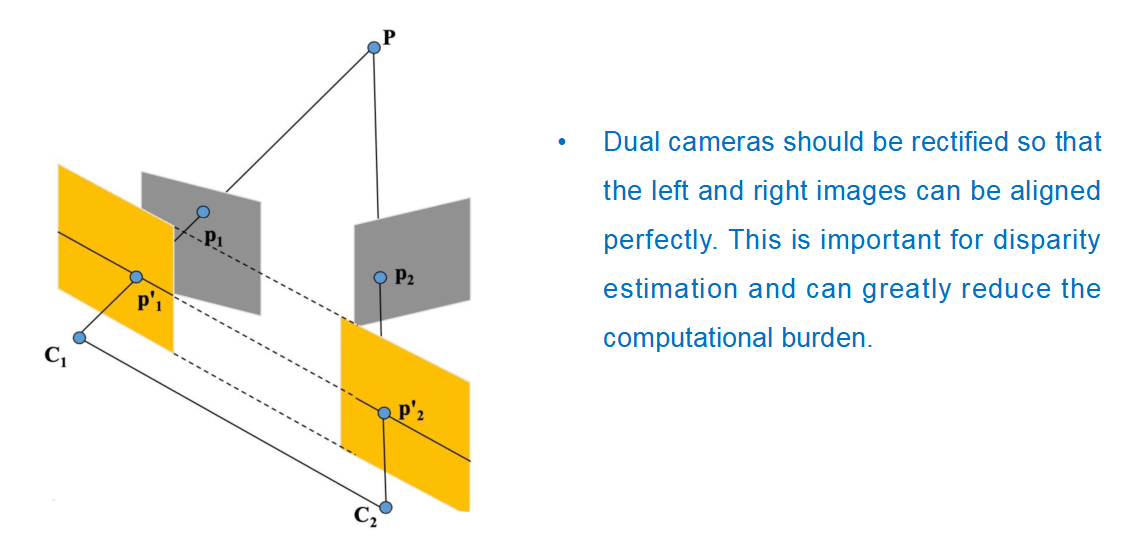
Please check the equation in the following picture.
The principle of the equation. when the camera keeps the same distance between object A and object B. in the picture after shooting,object A will be will be scaled down to length C. and the object B will be scaled down to length D. Since the camera is shooting A and B at the same shooting distance, so the ratio of reduction of A and B is the same.
When the reduction ratio of A and B is the same, we know the actual length and pixel value of A, and the actual value of B can be inferred from the equation of the reduction ratio.
The most important condition for the existence of this equation . A and B are shot at the same shooting distance. So, as long as A and B are in the same plane, the shooting distance of A and B must be the same, so we called 2D Plane contrast measurement.
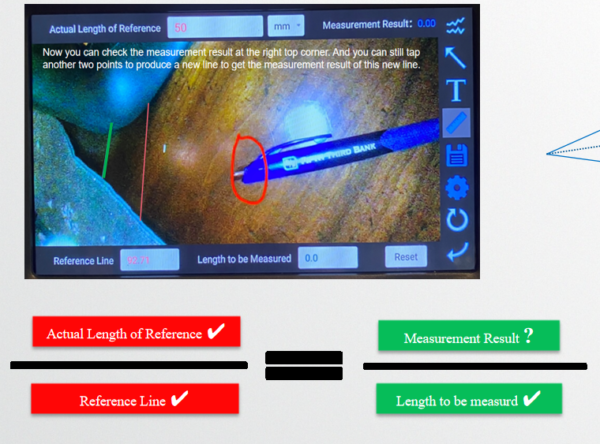
In the below picture, we know the actual value of the red line part, enter the actual value into the 【Actual value for reference】, then we can get the 【measurement value】
Please note that the result of the measurement is accurate. as long as the actual value is accurate, then the measurement value must be accurate.
If the actual value we know is biased, then the result must also be biased.
You could try to draw two lines on white paper first, and then measure the length of one line.
Then enter the actual value into the Q series. you will get a measurement value to check whether the date is accurate.