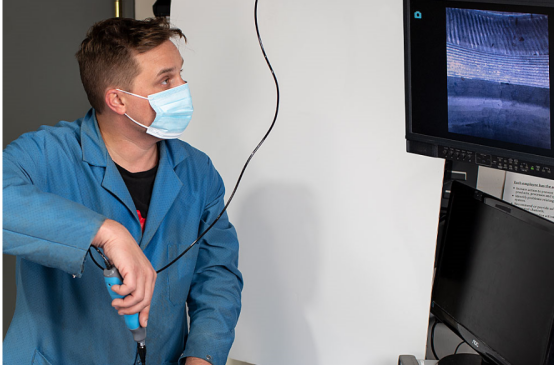
1.Whats is the borescope?
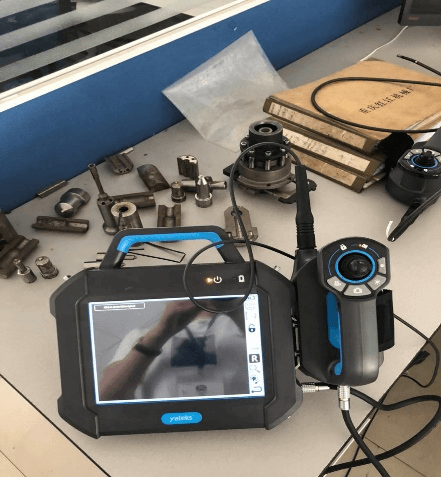
A borescope inspection is a non-destructive testing method that involves using a flexible or rigid tube with an attached camera and lighting system to visually inspect the interior of hard-to-reach areas or equipment. The borescope allows operators to view and capture images or videos of the inspected area, providing valuable visual information without the need for disassembly or invasive procedures. Borescope inspections are commonly used in industries such as aviation, automotive, manufacturing, plumbing, and more, to assess the condition, identify defects, and ensure proper functioning of equipment or structures.
2.The Importance of Regular Maintenance
1. Equipment Reliability:
Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they turn into major problems. This proactive approach reduces the risk of unexpected equipment failures and downtime, ensuring that the equipment remains reliable and operational.
2. Enhanced Safety:
Proper maintenance ensures that equipment is in optimal condition, minimizing the risk of accidents or malfunctions that could result in injuries to personnel or damage to property. Regular inspections and maintenance help identify and rectify any safety hazards or non-compliance issues.
3. Cost Savings:
Routine maintenance can help extend the lifespan of equipment by identifying and addressing minor issues promptly. This prevents the need for costly repairs or premature replacements. Moreover, regular maintenance reduces the likelihood of major breakdowns, which can be significantly more expensive to fix.
4. Energy Efficiency:
Well-maintained equipment operates more efficiently, reducing energy consumption and associated costs. Regular maintenance includes tasks like cleaning, lubricating, and calibrating equipment, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
5.Compliance with Regulations:
Many industries have regulations and standards in place that require regular inspections and maintenance of equipment. Adhering to these regulations helps organizations avoid legal issues, penalties, and reputational damage.
6.Improved Performance:
Regular maintenance helps equipment operate at peak performance levels. This can lead to improved productivity, better product quality, and a smoother workflow.
7. Warranty Protection:
Many equipment warranties require regular maintenance to remain valid. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule ensures that the warranty coverage remains intact, providing additional financial protection.
Overall, regular maintenance is essential for maximizing the lifespan, reliability, and safety of equipment. It is a proactive approach that saves costs, enhances performance, and minimizes risks associated with equipment failures.
3. Applications of Borescope Inspections in Different Industries
1. Aviation:
Borescope inspections are commonly used in aviation for inspecting aircraft engines. They allow maintenance personnel to visually assess the condition of engine components, such as turbine blades, combustion chambers, and fuel nozzles, without the need for disassembly. This helps identify any signs of wear, damage, or foreign object debris that could affect engine performance and safety.
2. Automotive:
In the automotive industry, borescope inspections are used for examining the internal components of engines, cylinders, and exhaust systems. This enables technicians to identify issues like carbon buildup, valve damage, piston problems, or leaks, allowing for timely repairs and maintenance.
3. Manufacturing:
Borescope inspections play a vital role in manufacturing industries. They are used to inspect the internal components of machinery, such as pumps, valves, turbines, and boilers. By visually examining these components, maintenance teams can identify wear, corrosion, blockages, or other issues that might affect efficiency and reliability.
4. Plumbing:
Borescope inspections are helpful in plumbing for investigating pipes, drains, and sewer systems. The flexible nature of borescopes allows them to navigate through pipes and provide visual feedback on blockages, leaks, corrosion, or other damages. This aids in diagnosing problems and planning appropriate repairs or maintenance.
5. Power Generation:
Borescope inspections are utilized in the power generation industry to examine various equipment, including turbines, generators, and heat exchangers. By inspecting the internal components, such as blades, rotors, or tubes, maintenance teams can identify issues like erosion, cracking, deposits, or other abnormalities that could impact system performance and efficiency.
6. Construction:
In the construction sector, borescope inspections are used to assess the condition of structures, such as walls, ceilings, or underground pipes. These inspections help detect hidden defects, such as cracks, leaks, or insulation issues, allowing for prompt repairs or preventive measures to ensure structural integrity.
7. Research and Development
Borescope inspections are also employed in research and development settings to observe and analyze the internal workings of experimental equipment or prototypes. This enables researchers to gain insights into performance, functionality, or potential areas of improvement.
These are just a few examples of how borescope inspections are applied in different industries. The versatility and non-destructive nature of borescope technology make it a valuable tool for visual inspection and maintenance across a wide range of sectors.
4. Training and Certification for Borescope Operators
1. Basic Knowledge
Operators should receive comprehensive training on the basic principles of borescope operation, including understanding the different types of borescopes, their components, and how to handle and maintain them properly.
2. Equipment Familiarization
Training should cover the specific borescope equipment used in the organization, including its features, controls, and functions. Operators should become familiar with adjustments such as focus, lighting, zoom, and image capture.
3. Inspection Techniques
Operators need to learn proper inspection techniques, including how to navigate the borescope through tight spaces, how to interpret images and videos, and how to identify common defects or abnormalities. They should understand best practices for capturing clear images and videos for documentation purposes.
4. Safety Procedures
Safety training is crucial to ensure that operators understand potential hazards associated with borescope inspections and how to mitigate risks. This includes proper handling of the equipment, following safety protocols, and using personal protective equipment (PPE) as necessary.
5. Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Operators should receive training on basic troubleshooting techniques to address common issues that may arise during inspections. They should also understand routine maintenance procedures, such as cleaning and calibrating the borescope, to ensure optimal performance.
6. Industry Standards and Regulations
Training should cover relevant industry standards and regulations that govern borescope inspections in specific sectors. Operators need to be aware of any legal requirements or guidelines to ensure compliance during their inspections.
7. Practical Hands-on Experience
Training should include practical sessions where operators can practice using the borescope equipment in realistic scenarios. This allows them to gain confidence and proficiency in operating the equipment and conducting inspections effectively.
Certification for borescope operators may be offered by professional organizations, equipment manufacturers, or training institutions. Certification typically involves a combination of training, written exams, and practical assessments to validate an operator’s knowledge and skills. Obtaining certification demonstrates that an operator has met certain standards and is qualified to perform borescope inspections competently.
Continuing education and regular refreshers are also recommended to keep operators updated on the latest advancements in borescope technology, inspection techniques, and safety protocols. This ensures that operators maintain their skills and knowledge over time and can adapt to evolving industry requirements.
In conclusion, routine borescope inspections are of utmost importance in various industries. They contribute to prevention, precision, compliance, and data-driven decision-making. By investing in regular inspections, businesses can ensure the longevity, efficiency, and safety of their equipment and operations. With the aid of borescopes, professionals can identify and address potential issues before they escalate, leading to enhanced productivity, reduced costs, and improved overall performance.